
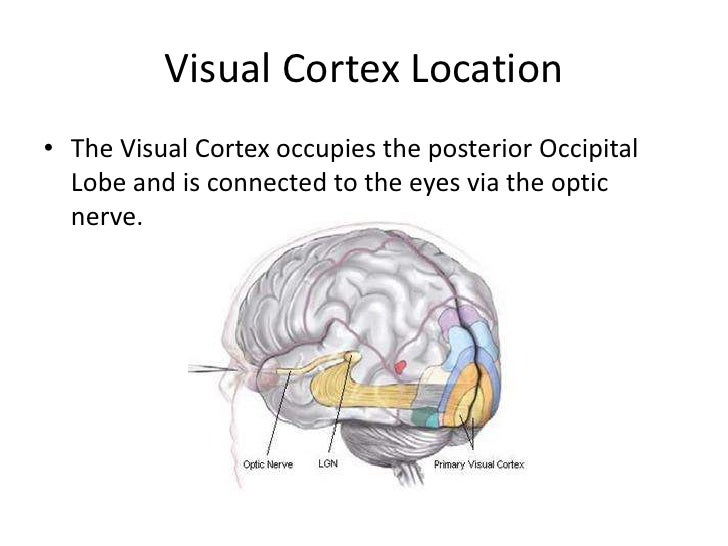
It is located in the most posterior region of the brain, posterior to the parietal lobe and temporal lobe. The occipital lobe is the smallest lobe in the cerebrum cortex. The medial temporal lobe (memory system) is still an active research area more precisely, the exact function of each structure in this lobe is currently being studied. Įpisodic memory is the type of memory that specializes in recalling an event and its associated details this is different from recognition memory, in which someone can consciously memorialize a specific event that happened throughout their life without being exposed to a similar situation. The lateral surface of the STG is thought to be the secondary auditory cortex that also functions in interpreting sounds, but mostly in the activities that involve task requirements. Researchers found that this process is not a simple task, but moreover, it is a complex task that is distributed all over the brain. The primary function of this area is the phonological representation, a process where the pronounced word is interpreted based on their tones and sound and trying to link it to a previously learned sound. The STP has another important area next to the HG called Wernicke’s area. In the past, this area was thought to have a significant role in speech perception and comprehension, but recent evidence shows that this area is not involved in this process. It is responsible for translating and processing all sounds and tones, and it is minimally affected by task requirements. Task requirement: a test where the examiner pronounces some words and asks the participant to categorize them acoustically, or phonemically, or semantically. The most significant anatomical landmark in STP is the Heschl gyrus (HG) which contains the primary auditory cortex. The STP is located deep in the Sylvain fissure. The superior temporal gyrus (STG) is further sub-divided into two surfaces, the dorsal surface (superior temporal plane STP) and the lateral surface of the STG.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
